Explore the world of web development through tutorials, best practices, and hands-on examples. Dive into frameworks, design principles, and coding challenges to level up your skills.
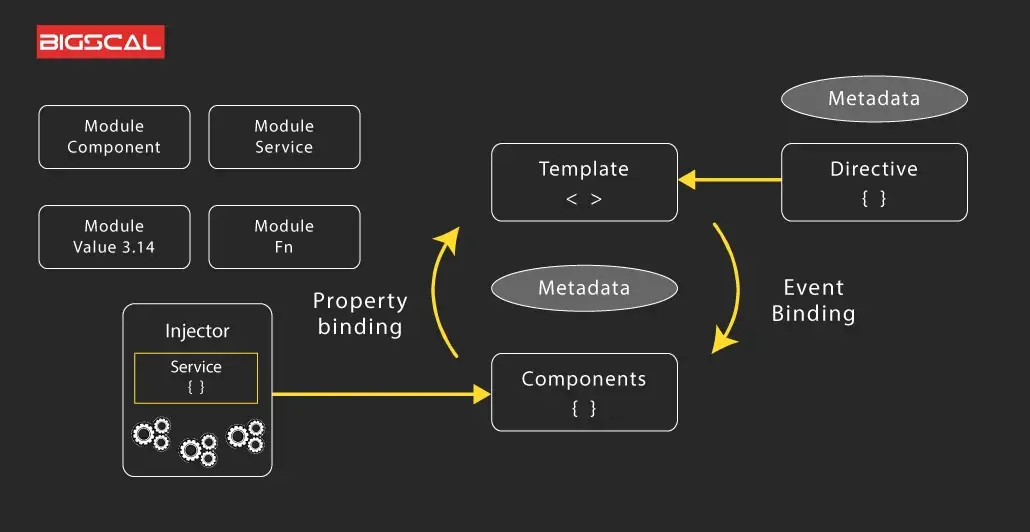
Table of contents [Show]
Angular Essentials: Building Scalable Apps with Components and Services
Introduction
Angular is a powerhouse framework for building dynamic, enterprise-grade web applications. Unlike React or Vue, Angular provides a full-stack solution with built-in tools for routing, state management, and dependency injection. In this guide, we’ll explore Angular’s component-based architecture, services, and how to structure scalable apps.
Why Choose Angular?
- Opinionated architecture for team consistency
- Two-way data binding for seamless UI updates
- Robust CLI for scaffolding and deployment
- Integrated support for TypeScript
Core Concepts in Angular
1. Components: The UI Building Blocks
Components combine HTML templates with TypeScript logic. Use the Angular CLI to generate them:
ng generate component user-profile
A basic component:
// user-profile.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-user-profile',
template: `
<div>
<h2>{{ username }}</h2>
<p>Joined: {{ joinDate | date }}</p>
</div>
`,
})
export class UserProfileComponent {
username = 'Alice';
joinDate = new Date(2020, 1, 15);
}2. Services and Dependency Injection
Services handle business logic and data fetching. Angular’s DI system injects them into components:
// data.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class DataService {
fetchUsers() {
return ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'];
}
}
// app.component.ts
export class AppComponent {
users: string[];
constructor(private dataService: DataService) {
this.users = this.dataService.fetchUsers();
}
}3. Modules: Organizing Your App
Angular apps are modular. Use NgModule to bundle components, services, and routes:
// app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { UserProfileComponent } from './user-profile.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [UserProfileComponent],
imports: [BrowserModule],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule {}Example: Task Manager App
Let’s build a simple task manager using Angular’s features:
// task.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-task-list',
template: `
<div>
<input [(ngModel)]="newTask" placeholder="Add task">
<button (click)="addTask()">Add</button>
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let task of tasks">{{ task }}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`,
})
export class TaskListComponent {
tasks: string[] = [];
newTask = '';
addTask() {
if (this.newTask.trim()) {
this.tasks.push(this.newTask);
this.newTask = '';
}
}
}Angular CLI: Your Productivity Booster
Key commands to speed up development:
ng new my-app // Create new project
ng serve // Start dev server
ng generate service api// Generate a service
ng build --production // Optimized buildBest Practices
- Use lazy loading for large apps
- Leverage RxJS for reactive programming
- Implement route guards for authentication
- Adopt standalone components (Angular 15+)
Conclusion
Angular’s structured approach makes it ideal for complex applications. By mastering components, services, and modules, you can create maintainable apps that scale effortlessly. Pair it with TypeScript and RxJS, and you’ll unlock a world of type-safe, reactive programming. Ready to architect your next big project? Angular has your back!