CodeCraft Chronicles is your go-to resource for mastering modern web development technologies. From beginner-friendly tutorials to advanced coding techniques, we cover everything you need to build scalable, efficient, and visually stunning web applic...
Getting Started with React: A Beginner's Guide to Building Modern Web Applications
React is a powerful JavaScript library for building user interfaces, developed and maintained by Facebook. It’s widely used for creating dynamic, high-performance web applications. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, React’s component-based architecture and declarative syntax make it a joy to work with. In this guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of React and walk you through building your first React application.
Table of contents [Show]
What is React?
React is an open-source JavaScript library designed for building user interfaces, particularly single-page applications (SPAs). It allows developers to create reusable UI components and efficiently update the user interface as data changes. React’s virtual DOM ensures optimal performance by minimizing direct manipulation of the actual DOM.
Key Features of React
- Component-Based Architecture: Break down your UI into reusable components for better organization and maintainability.
- Declarative Syntax: Describe what your UI should look like for different states, and React will handle the rendering.
- Virtual DOM: Improves performance by updating only the parts of the DOM that have changed.
- Unidirectional Data Flow: Data flows from parent to child components, making it easier to debug and understand.
- Rich Ecosystem: A vast collection of libraries and tools, such as React Router and Redux, extend React’s capabilities.
Setting Up Your First React App
To get started with React, you’ll need Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager) installed on your machine. Follow these steps to create a new React project:
- Install
create-react-app, a tool for setting up a React project:
npx create-react-app my-first-react-app
- Navigate to the project directory and start the development server:
cd my-first-react-app
npm start
Open your browser and visit http://localhost:3000 to see your React app in action.
Understanding React Components
React applications are built using components, which are reusable pieces of code that represent parts of the UI. There are two types of components: functional components and class components. Let’s create a simple functional component:
import React from 'react';
function Welcome(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}!</h1>;
}
export default Welcome;
To use this component, import and render it in your App.js file:
import React from 'react';
import Welcome from './Welcome';
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Welcome name="React Developer" />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
This will display "Hello, React Developer!" on the screen.
State and Props in React
Props (short for properties) are used to pass data from parent to child components. They are read-only and help make components dynamic. State, on the other hand, is used to manage data that changes over time within a component.
Here’s an example of a component using state:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
}
export default Counter;
This component maintains a count state and updates it when the button is clicked.
Conclusion
React is a versatile and powerful library for building modern web applications. Its component-based architecture, declarative syntax, and performance optimizations make it a favorite among developers. By following this guide, you’ve learned the basics of React, including setting up a project, creating components, and managing state and props. Start building your next project with React today!
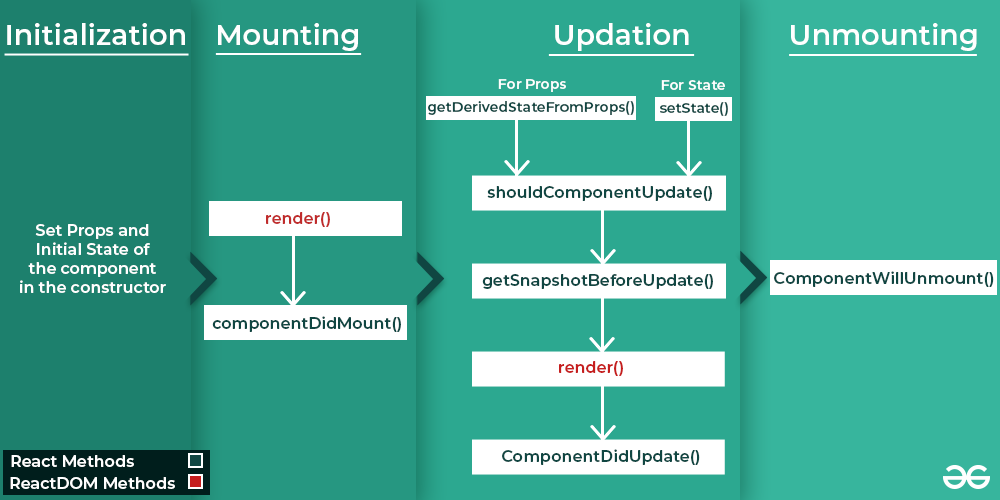
Suggested Image Title: "React Component Lifecycle Diagram"